Rayrai Example: LiDAR Pointcloud
Overview
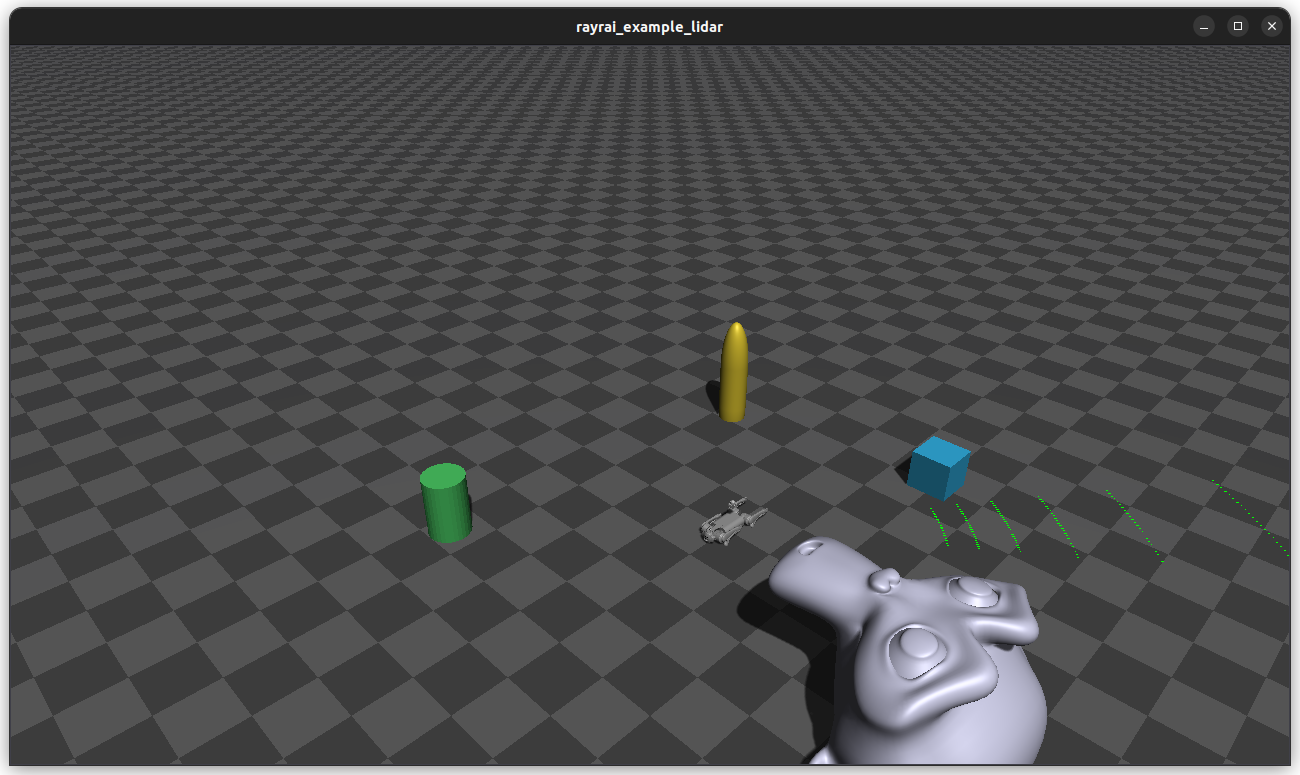
Attaches a Livox LiDAR module to Go1 and visualizes the scan as a point cloud every frame, with nearby primitives and a static mesh to generate richer returns.
Screenshot
Binary
CMake target and executable name: rayrai_lidar_pointcloud.
Run
Build and run from your build directory:
cmake --build . --target rayrai_lidar_pointcloud
./rayrai_lidar_pointcloud
On Windows, run rayrai_lidar_pointcloud.exe instead.
This example uses the in-process rayrai renderer (no external client required).
Details
Loads Go1 with a Livox LiDAR module and updates scans each frame.
Transforms LiDAR points from sensor to world frame.
Visualizes the scan as a point cloud with adjustable point size.
Source
#include <cmath>
#include <memory>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <glm/glm.hpp>
#include "rayrai/example_common.hpp"
#include "rayrai_example_resources.hpp"
#include "raisim/World.hpp"
static inline glm::dvec3 toGlm(const raisim::Vec<3>& v) {
return glm::dvec3(v[0], v[1], v[2]);
}
static inline glm::dmat3 toGlm(const raisim::Mat<3, 3>& R) {
return glm::dmat3(glm::dvec3(R(0, 0), R(1, 0), R(2, 0)), glm::dvec3(R(0, 1), R(1, 1), R(2, 1)),
glm::dvec3(R(0, 2), R(1, 2), R(2, 2)));
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
ExampleApp app;
if (!app.init("rayrai_example_lidar", 1280, 720))
return -1;
auto world = std::make_shared<raisim::World>();
world->addGround();
const std::string sep = raisim::Path::separator();
const std::string go1Dir = rayraiRscPath(argv[0], "go1");
std::vector<std::string> modules = {"livox_lidar"};
auto go1 = world->addArticulatedSystem(go1Dir + sep + "go1.urdf", modules, go1Dir);
go1->setGeneralizedCoordinate({0, 0, 0.32, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0, 0.67, -1.3, 0, 0.67, -1.3, 0,
0.67, -1.3, 0, 0.67, -1.3});
auto lidar = go1->getSensorSet("livox_lidar_0")->getSensor<raisim::SpinningLidar>("lidar");
auto sphere = world->addSphere(0.2, 1);
sphere->setPosition(2.5, 2.0, 0.6);
sphere->setAppearance("0.9,0.3,0.2,1.0");
auto box = world->addBox(0.4, 0.4, 0.4, 1);
box->setPosition(-2.0, 1.0, 0.4);
box->setAppearance("0.2,0.7,0.9,1.0");
auto cylinder = world->addCylinder(0.2, 0.6, 1);
cylinder->setPosition(1.8, -1.8, 0.3);
cylinder->setAppearance("0.3,0.8,0.4,1.0");
auto capsule = world->addCapsule(0.15, 0.5, 1);
capsule->setPosition(-1.6, -1.3, 0.45);
capsule->setAppearance("0.9,0.8,0.2,1.0");
std::string monkeyFile = rayraiRscPath(argv[0], "monkey/monkey.obj");
raisim::Mat<3, 3> inertia;
inertia.setIdentity();
const raisim::Vec<3> com = {0, 0, 0};
auto monkey = world->addMesh(monkeyFile, 1.0, inertia, com);
monkey->setPosition(0.8, 2.2, 0.35);
monkey->setAppearance("0.8,0.8,0.9,1.0");
monkey->setBodyType(raisim::BodyType::STATIC);
auto viewer = std::make_shared<raisin::RayraiWindow>(world, 1280, 720);
viewer->setBackgroundColor({25, 25, 35, 255});
auto lidarCloud = viewer->addPointCloud("lidar_scan");
if (lidarCloud) {
lidarCloud->pointSize = 3.0f;
lidarCloud->setDetectable(true);
}
while (!app.quit) {
app.processEvents();
if (app.quit)
break;
world->integrate();
lidar->updatePose();
const glm::dvec3 sensorPosW = toGlm(lidar->getPosition());
const glm::dmat3 sensorRotW = toGlm(lidar->getOrientation());
lidar->update(*world);
if (lidarCloud) {
const auto& scanS = lidar->getScan();
lidarCloud->positions.clear();
lidarCloud->colors.clear();
lidarCloud->positions.reserve(scanS.size());
lidarCloud->colors.reserve(scanS.size());
const glm::vec4 kColor(0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f);
for (const auto& ps : scanS) {
const glm::dvec3 pS(ps[0], ps[1], ps[2]);
const glm::dvec3 pW = sensorRotW * pS + sensorPosW;
lidarCloud->positions.emplace_back(glm::vec3(pW));
lidarCloud->colors.emplace_back(kColor);
}
lidarCloud->updatePointBuffer();
}
app.beginFrame();
app.renderViewer(*viewer);
app.endFrame();
}
viewer.reset();
app.shutdown();
return 0;
}