Server Example: Material Restitution
Overview
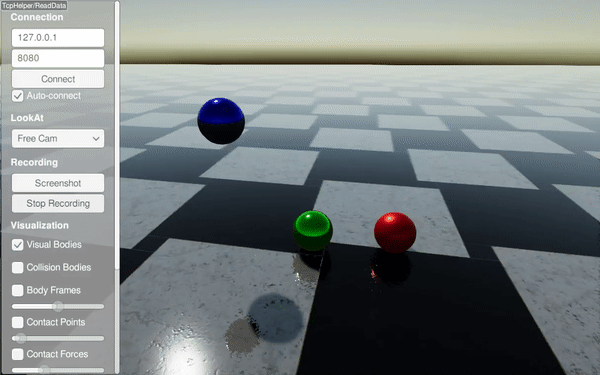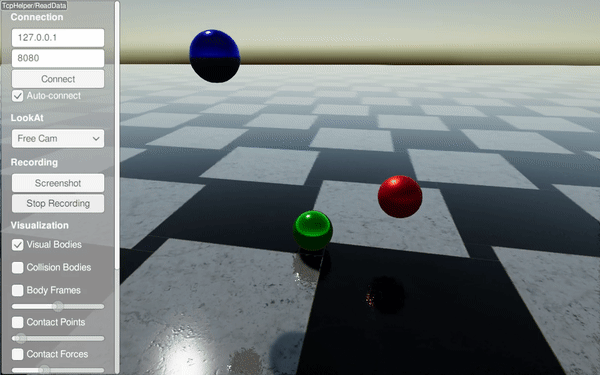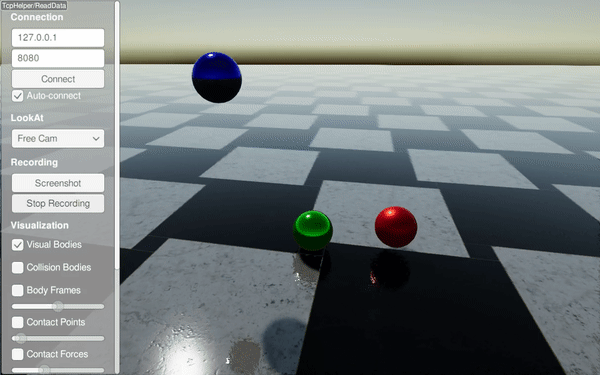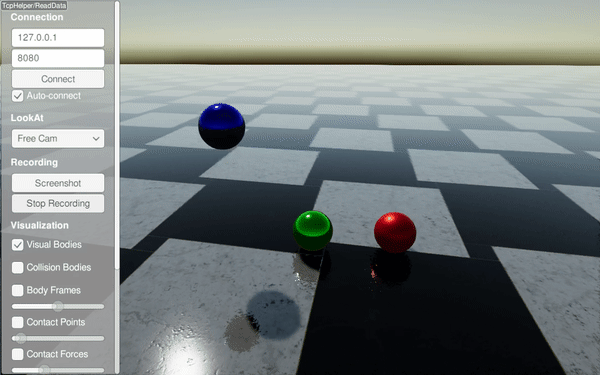
Drops spheres with different material labels (steel, rubber, copper) and configures material pair properties. It highlights restitution and friction differences.
Screenshot
Binary
CMake target and executable name: material_restitution.
Run
Build and run from your build directory:
cmake --build . --target material_restitution
./material_restitution
On Windows, run material_restitution.exe instead.
This example uses RaisimServer. Start a visualizer client (RaisimUnity, RaisimUnreal, or the rayrai TCP viewer) and connect to port 8080.
Details
Drops three spheres with different materials onto a steel ground.
Sets per-material restitution to compare bounce behavior.
Reference for
World::setMaterialPairProprestitution settings.
Source
// This file is part of RaiSim. You must obtain a valid license from RaiSim Tech
// Inc. prior to usage.
#include "raisim/RaisimServer.hpp"
#include "raisim/World.hpp"
#include "rayrai_tcp_viewer_hint.hpp"
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
auto binaryPath = raisim::Path::setFromArgv(argv[0]);
/// create raisim world
raisim::World world;
world.setTimeStep(0.001);
/// create objects
world.addGround(0, "steel");
auto sphere1 = world.addSphere(0.5, 1.0, "steel");
auto sphere2 = world.addSphere(0.5, 1.0, "rubber");
auto sphere3 = world.addSphere(0.5, 1.0, "copper");
sphere1->setPosition(-2,0,5);
sphere2->setPosition(0,0,5);
sphere3->setPosition(2,0,5);
world.setMaterialPairProp("steel", "steel", 0.8, 0.95, 0.001);
world.setMaterialPairProp("steel", "rubber", 0.8, 0.15, 0.001);
world.setMaterialPairProp("steel", "copper", 0.8, 0.65, 0.001);
/// launch raisim server
raisim::RaisimServer server(&world);
server.launchServer();
raisim_examples::warnIfNoClientConnected(server);
for (int i = 0; i < 5000; i++) {
RS_TIMED_LOOP(int(world.getTimeStep()*1e6))
server.integrateWorldThreadSafe();
}
server.killServer();
}