Server Example: Templated Tracked Robot
Overview
Loads a templated tracked robot URDF with parameter overrides and drives wheels/flippers using PD targets. It shows how to customize URDF parameters programmatically.
Screenshot
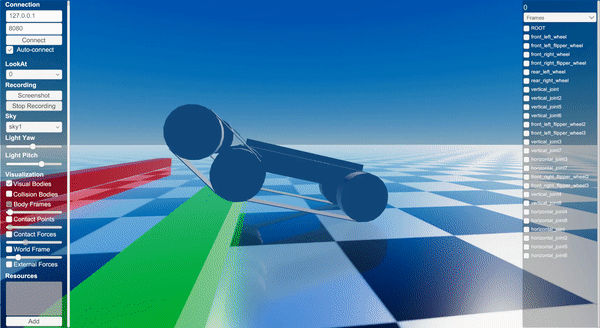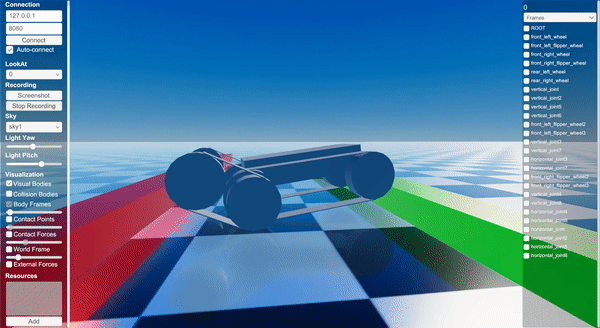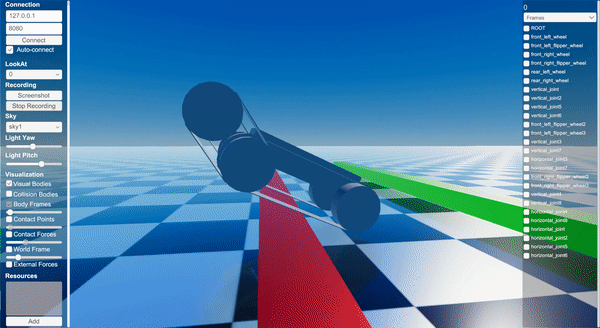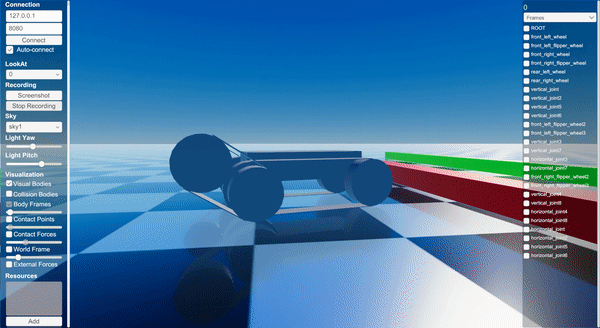
Binary
CMake target and executable name: templated_tracked_robot.
Run
Build and run from your build directory:
cmake --build . --target templated_tracked_robot
./templated_tracked_robot
On Windows, run templated_tracked_robot.exe instead.
This example uses RaisimServer. Start a visualizer client (RaisimUnity, RaisimUnreal, or the rayrai TCP viewer) and connect to port 8080.
Details
Instantiates a templated tracked robot URDF with parameter overrides.
Applies PD control to wheels and flippers while resetting track joints.
Adds a sequence of box obstacles in front of the robot.
Source
// This file is part of RaiSim. You must obtain a valid license from RaiSim Tech
// Inc. prior to usage.
#include "raisim/RaisimServer.hpp"
#include "raisim/World.hpp"
#include "rayrai_tcp_viewer_hint.hpp"
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
auto binaryPath = raisim::Path::setFromArgv(argv[0]);
raisim::World world;
world.setTimeStep(0.001);
/// create raisim environment
world.addGround();
auto box1 = world.addBox(1,3,0.3, 100);
box1->setPosition(2, 0, 0.15);
auto box2 = world.addBox(1,3,0.2, 100);
box2->setPosition(4, 0, 0.1);
auto box3 = world.addBox(1,3,0.3, 100);
box3->setPosition(6, 0, 0.15);
auto box4 = world.addBox(1,3,0.2, 100);
box4->setPosition(8, 0, 0.1);
auto box5 = world.addBox(1,3,0.3, 100);
box5->setPosition(10, 0, 0.15);
/// customize robot in code
std::vector<raisim::World::ParameterContainer> params;
params.push_back({"rho", "500"});
params.push_back({"base_length", "1.0"});
params.push_back({"base_width", "0.15"});
params.push_back({"wheel_y_offset", "0.14"});
params.push_back({"track_y_offset", "0.24"});
params.push_back({"wheel_width", "0.08"});
params.push_back({"wheel_radius", "0.17775"});
params.push_back({"flipper_radius", "0.16"});
auto robot =
world.addArticulatedSystem(binaryPath.getDirectory() + "/rsc/templatedTrackedRobot/trackedTemplate.urdf", params);
robot->setName("tracked");
robot->setBasePos({0,0,0.4});
Eigen::VectorXd pGain(robot->getDOF()), dGain(robot->getDOF()), pTarget(robot->getGeneralizedCoordinateDim()),
dTarget(robot->getDOF());
raisim::Vec<3> pos(robot->getBasePosition());
pGain.setZero();
dGain.setZero();
pTarget.setZero();
dTarget.setZero();
std::vector<int> trackLinkGv = {10, 12, 18, 20, 24, 26, 28, 30, 11, 13, 19, 21, 25, 27, 29, 31};
std::vector<int> wheelGv = {6, 22, 14, 23, 8, 9, 16, 17};
std::vector<int> flipperGv = {7, 15};
dGain.setConstant(50.0);
for (auto wheel: wheelGv)
dTarget[wheel] = 5.0;
for (auto flipper: flipperGv) {
pGain[flipper] = 250.0;
pTarget[flipper + 1] = -0.6;
}
/// launch raisim server
raisim::RaisimServer server(&world);
server.launchServer();
raisim_examples::warnIfNoClientConnected(server);
server.focusOn(robot);
for (int i = 0; i < 200000; i++) {
RS_TIMED_LOOP(int(world.getTimeStep()*1e6))
raisim::VecDyn gc = robot->getGeneralizedCoordinate();
raisim::VecDyn gv = robot->getGeneralizedVelocity();
// reset tracks
for (auto idx : trackLinkGv) {
gc[idx + 1] = 0;
gv[idx] = 0;
pGain[idx] = 0;
dGain[idx] = 0;
}
robot->setState(gc.e(), gv.e());
robot->setPdGains(pGain, dGain);
robot->setPdTarget(pTarget, dTarget);
server.integrateWorldThreadSafe();
}
server.killServer();
}